HOME >
Technical Information > How to Use GOHSENOL™ > Storage of Aqueous Solutions
Technical Information
How to Use GOHSENOL™
Storage of Aqueous Solutions
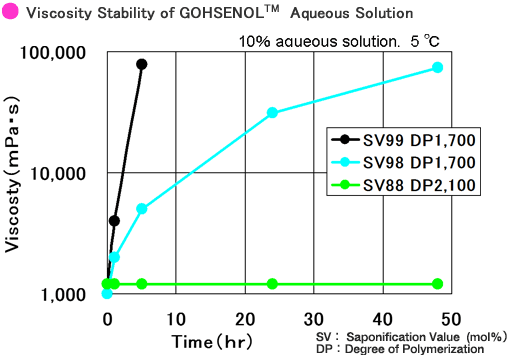
- An aqueous solution of N- or A-type GOHSENOL™ usually increases viscosity or causes gelation
when left alone. A lower temperature and higher saponification degree will make this tendency more
remarkable. If the aqueous solution contains GOHSENOL™ alone, it usually returns to its former
state when the temperature is raised.
- G- or K-type GOHSENOL™ is less likely to gelate than N- and A-type (hardly gelate even at a
higher concentration). Sorbic acid, rhodan salt, or a higher alcohol is effective for preventing
gelation if it is slight.
- Do not use containers that easily rust. Sodium nitrite or sodium benzoate is effective for the
prevention of rust.
- Mildew rarely grows in aqueous solutions of GOHSENOL™.
- Sodium dehydroacetate, potassium sorbate, and sodium pentachlorophenol effective preservatives
(0.01-0.1 weight % to an aqueous solution of GOHSENOL™ is suitable).
- In the case of adding rust inhibitors or preservatives, be sure to refer to the instruction manuals
provided for the chemicals.